Live Data Feedback: How DVS Heat Transfer Systems Enable Predictive Maintenance
A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Transfer Equipments for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate Heat transfer system is vital for operational efficiency. Various systems accommodate various requirements, affected by factors such as temperature range and liquid type. Understanding the concepts behind Heat transfer, such as radiation, conduction, and convection, is essential. Additionally, reviewing energy resources and upkeep practices can influence long-lasting efficiency. A closer assessment of these factors to consider discloses just how to tailor a system to specific demands. What should one prioritize in this complex decision-making procedure?
Comprehending Heat Transfer: Secret Concepts and Principles
Heat transfer might appear like a simple idea, it includes a range of principles that are essential for reliable system layout - DVS Heat Transfer Systems. Recognizing these principles is crucial for designers and developers who aim to enhance thermal efficiency in various applications. Conduction, for example, includes the transfer of Heat via solid products, while convection describes the movement of Heat within fluids. Radiation, one more essential principle, explains just how Heat can be transferred through electromagnetic waves. Each of these devices plays a vital duty in figuring out exactly how energy relocates within a system. By completely comprehending these ideas, experts can make educated decisions, guaranteeing that Heat transfer systems operate effectively and meet the specific demands of their applications
Kinds of Heat Transfer Equipments: An Overview
Recognizing the concepts of Heat transfer prepares for exploring the different types of Heat transfer systems offered. Heat transfer systems can be categorized mainly into 3 kinds: conduction, radiation, and convection. Conduction includes Heat transfer via solid products, relying upon straight contact between bits. Convection, on the other hand, occurs in fluids (liquids and gases) where the movement of the liquid itself promotes Heat transfer. Radiation entails the transfer of Heat through electro-magnetic waves and does not call for a medium, allowing it to take place in a vacuum. Each sort of system has distinct features and applications, making it necessary for individuals and organizations to thoroughly examine their details requirements when choosing the most ideal Heat transfer solution.
Applications of Heat Transfer Systems in Numerous Industries
Heat transfer systems play an important duty across different industries, affecting efficiency and product top quality. In industrial manufacturing processes, they facilitate accurate temperature control, while in food and drink handling, they guarantee security and preservation. In addition, a/c and environment control systems rely heavily on reliable Heat transfer to preserve comfortable environments.
Industrial Production Processes

Many industrial manufacturing procedures rely greatly on efficient Heat transfer systems to make best use of efficiency and enhance item top quality. In sectors such as metalworking, Heat exchangers play a crucial function in maintaining ideal temperatures during welding, casting, and creating. These systems ensure consistent Heat distribution, which is vital for achieving preferred product homes. In the chemical production sector, Heat transfer systems promote precise temperature control during reactions, affecting yield and safety. Furthermore, in fabric manufacturing, effective Heat management is very important for dyeing and finishing procedures, affecting shade uniformity and material high quality. By choosing appropriate Heat transfer modern technologies, manufacturers can improve power effectiveness and decrease functional expenses, eventually leading to an extra lasting and affordable production environment.
Food and Drink Handling
Reliable Heat transfer systems are just as crucial in the food and drink handling industry, where preserving optimal temperatures is essential for food security and quality. These systems play an important role in procedures such as pasteurization, food preparation, and sterilization, making certain that products are risk-free for usage and preserve their nutritional worth. Heat exchangers, for example, efficiently move Heat between liquids, optimizing energy use while decreasing temperature changes. Additionally, refrigeration systems are essential for extending and protecting perishable products service life. The choice of Heat transfer technology directly affects functional efficiency and product honesty, making it essential for food and beverage suppliers to pick the suitable systems customized to their specific processing needs. This mindful choice inevitably contributes to consumer fulfillment and food safety.

Heating And Cooling and Climate Control
While many sectors depend on Heat transfer systems for efficiency, A/C (Heating, Ventilation, and Cooling) plays a necessary role in keeping interior environment control throughout various setups. These systems utilize Heat transfer principles to manage humidity, air, and temperature level high quality, making sure convenience and security in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Correctly designed cooling and heating systems improve energy effectiveness, minimize functional prices, and minimize environmental influence. In commercial buildings, for example, effective climate control contributes to employee productivity and client satisfaction. In commercial applications, heating and cooling systems help preserve ideal conditions for devices operation and product preservation. Selecting the appropriate Heat transfer system is vital for conference particular environment control demands and achieving general system performance.
Assessing Power Resources for Heat Transfer Systems
In evaluating energy sources for Heat transfer systems, a comparison of renewable energy options and nonrenewable fuel source considerations is important. Eco-friendly resources, such as solar and wind, deal sustainable options that can lower environmental impact. On the other hand, nonrenewable fuel sources continue to be widespread as a result of their well established facilities and power density, prompting a mindful evaluation of both choices.
Renewable Resource Options

Nonrenewable Fuel Source Considerations
Evaluating nonrenewable fuel source factors to consider is necessary for the performance and sustainability of Heat transfer systems. Nonrenewable fuel sources, such as natural gas, oil, and coal, are typical energy resources get redirected here that offer significant Heat outcome, making them preferred options for household and commercial applications. Their ecological influence, consisting of greenhouse gas discharges and source depletion, increases concerns. When picking a heat transfer system, it is essential to analyze the accessibility, expense, and regulatory variables connected with these fuels. Furthermore, the effectiveness of fossil gas systems must be considered, as higher performance can minimize some environmental disadvantages. Inevitably, check my site a well balanced approach considering efficiency and sustainability can lead decision-makers towards one of the most proper Heat transfer service for their details needs.
Variables to Think About When Picking a Warm Transfer System
Picking a suitable Heat transfer system needs cautious factor to consider of numerous variables that can substantially impact effectiveness and efficiency. One essential factor is the operating temperature variety, which dictates the materials and style appropriate for the application. Furthermore, the sort of liquid made use of in the system-- whether gas or fluid-- influences Heat transfer efficiency and compatibility. The system's size and capability have to straighten with the specific requirements of the procedure to stay clear of inadequacies. Power resource accessibility is likewise essential, influencing operating costs and sustainability. Additionally, the setup atmosphere, including room restraints and ease of access for upkeep, plays a substantial duty in system selection. Ultimately, regulatory conformity and safety and security criteria must be considered to assure the system meets all lawful requirements.
Maintenance and Efficiency Optimization for Heat Transfer Systems
Keeping Heat transfer systems is essential for making certain maximum efficiency and longevity. Routine upkeep activities, such as cleansing Heat exchangers and evaluating insulation, assistance prevent effectiveness losses as a result of fouling and thermal bridging. In addition, monitoring system criteria, including stress and temperature, permits early discovery of anomalies, lessening downtime and costly repairs. Carrying out a preventive upkeep schedule can optimize efficiency and extend the life expectancy of parts. Moreover, upgrading to innovative control systems can enhance operational effectiveness by getting used to varying problems and tons. By prioritizing maintenance and effectiveness optimization, operators can attain reduced energy usage, reduced operational prices, and improved overall system reliability, eventually causing far better resource utilization and a more sustainable operation.
Future Fads in Heat Transfer Technologies
As sectors increasingly prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, future patterns in Heat transfer innovations are set to go through considerable changes. Technologies such as innovative products, including carbon nanotubes and nanofluids, guarantee boosted thermal conductivity and performance. In addition, the combination of renewable resource sources into Heat transfer systems is getting momentum, promoting eco-friendly solutions. Smart technologies, consisting of IoT sensing units, are expected to change monitoring and control, allowing real-time information evaluation for optimized efficiency. Additionally, the advancement of compact and modular systems will certainly promote simpler installation and upkeep, dealing with diverse applications. These innovations suggest a change towards even more lasting, reliable, and adaptable Heat transfer options, straightening with global power goals and ecological requirements.
Frequently Asked Concerns
What Are the Environmental Influences of Heat Transfer Equipments?
The environmental influences of Heat transfer systems can consist of greenhouse gas discharges, energy intake, and potential thermal contamination. Additionally, incorrect disposal visit of products and ineffectiveness can add to resource exhaustion and environment disruption.
Just how Do I Determine the Cost-Effectiveness of a Warmth Transfer System?
To calculate the cost-effectiveness of a warmth transfer system, one should examine initial prices, functional expenses, maintenance demands, and energy efficiency, contrasting these aspects versus the expected lifespan and performance of the system.
Can Heat Transfer Systems Be Used in Residential Settings?
Heat transfer systems can without a doubt be made use of in residential setups. They supply efficient heating and cooling down remedies, making homes much more comfortable while potentially reducing power prices. Their flexibility enables different applications in residential settings.
What Safety Laws Relate To Heat Transfer Solutions?
Safety policies for Heat transfer systems usually consist of guidelines on maintenance, installation, and operation. Compliance with local building regulations, maker specs, and market criteria is vital to assure effective and safe system performance in various applications.
How Do Various Products Affect Heat Transfer Efficiency?
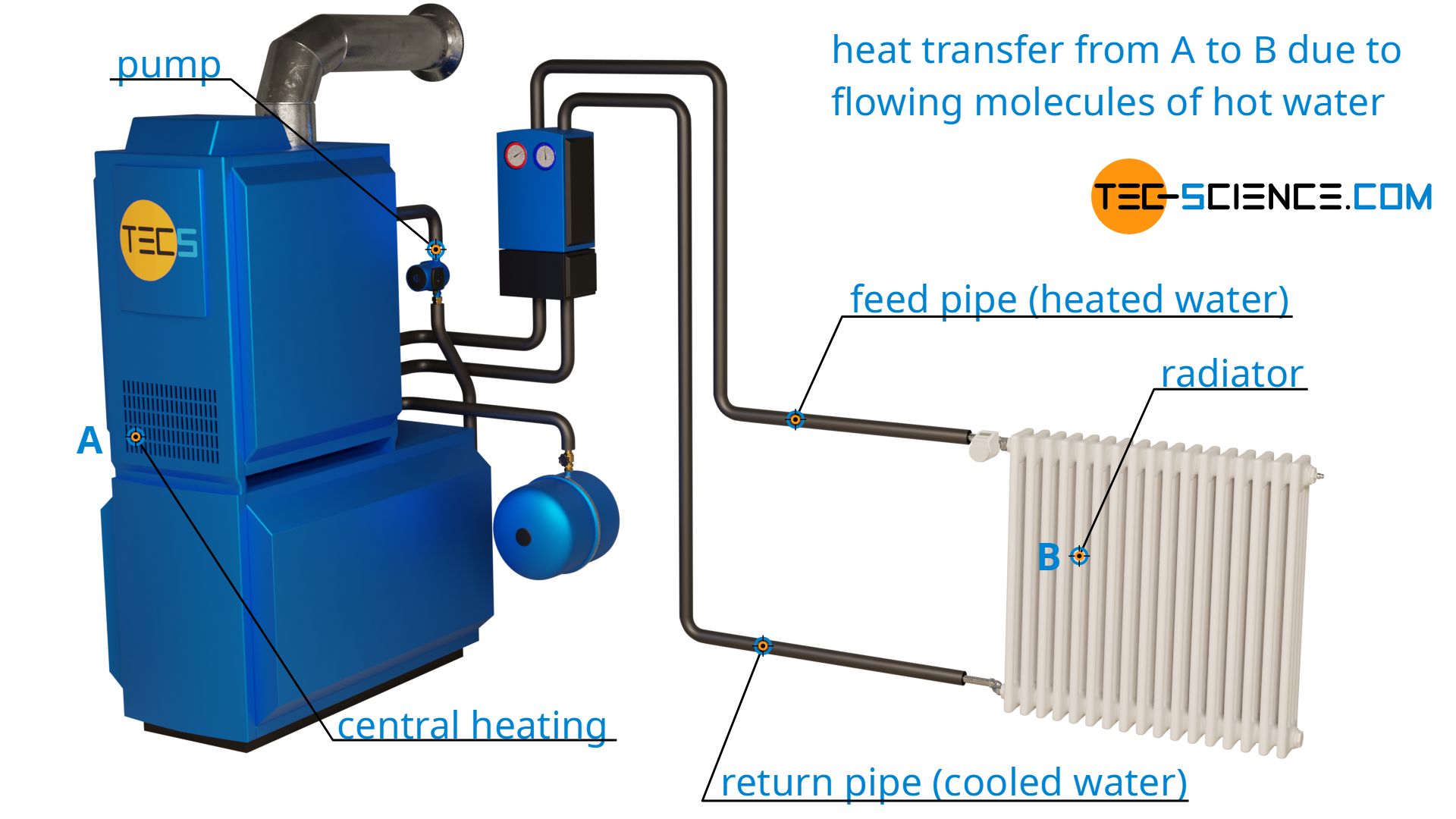
Conduction, for instance, involves the transfer of Heat with strong materials, while convection refers to the motion of Heat within liquids. Understanding the concepts of Heat transfer lays the foundation for exploring the various types of Heat transfer systems available. Heat exchangers, for circumstances, successfully move Heat between liquids, optimizing power use while decreasing temperature level variations. In reviewing power resources for Heat transfer systems, a contrast of eco-friendly power choices and fossil fuel considerations is necessary. Metals, such as copper and aluminum, conduct Heat properly, whereas insulators like rubber and glass reduce down Heat flow.